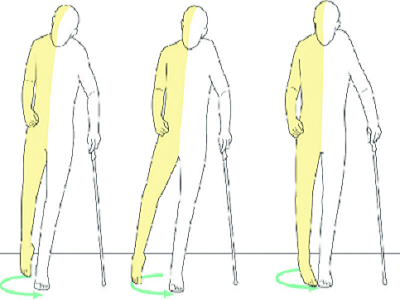
Common signs and symptoms of CMT
Symptoms commonly appear in adolescence or early adulthood but can be earlier or later. Living with CMT is a daily challenge which can, at times, lead to individuals developing signs of anxiety and depression.

CMT is caused by an inherited fault in one of the many genes responsible for the development of the peripheral nerves. This fault means the nerves become damaged over time.
A child with CMT may have inherited the genetic fault responsible for the condition from 1 or both of their parents. It could also be a new mutation.
Children as young as 3 months are now being been diagnosed with CMT. However, the symptoms of CMT usually start to appear between the ages of 5 and 15, although they sometimes do not develop until well into middle age or later.



Reading text is so boring? Let's watch this video to know more about CMT! We hope you really enjoy this video clip.

We developed this small questionnaire for all of you after watching the video. We hope you can spend a few minutes to finish this~
They are working to support those who are affected by Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. They offer assistance and support to people who have CMT and also initiate, co-ordinate, promote and support research into CMT and its effects. They also offer assistance and support to those who care for people who have CMT.
Should you wish to donate to CMT UK, please use the link below.